
A) Na reduction in the soil (%) by wicking material (hydraulic
4.7 (235) In stock

4.7 (235) In stock
Download scientific diagram | (A) Na reduction in the soil (%) by wicking material (hydraulic mulch [HM], Humidi‐Wick [HW], wheat straw [S], and Super Wick [SW]) and water table depth. Upper and lowercase letters represent significant differences in Na reduction for Water Table 1 (5 cm) and Water Table 2 (15 cm), respectively. Ratios of evaporation rate between each combination of wicking/water table treatments, and the control are shown above each boxplot. (B) Relationship between Na reduction (%) and daily evaporation rate (mL d⁻¹). (C) Initial and final electrical conductivity (EC) and %Na for Super Wick and Water Table 1. † %Na was calculated using the method presented in DeSutter et al. (2015). from publication: Wicking Salts from Brine-Contaminated Soils: A Potential Method for In Situ Remediation | Core Ideas “Wicking” salts from brine‐impacted soils may be an effective means of remediation. Wicking materials reduced the mass of Na in brine‐impacted soil columns up to 88%. This method may expedite remediation of brine‐impacted soils with shallow water | Capillarity, Remediation and In Situ | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.
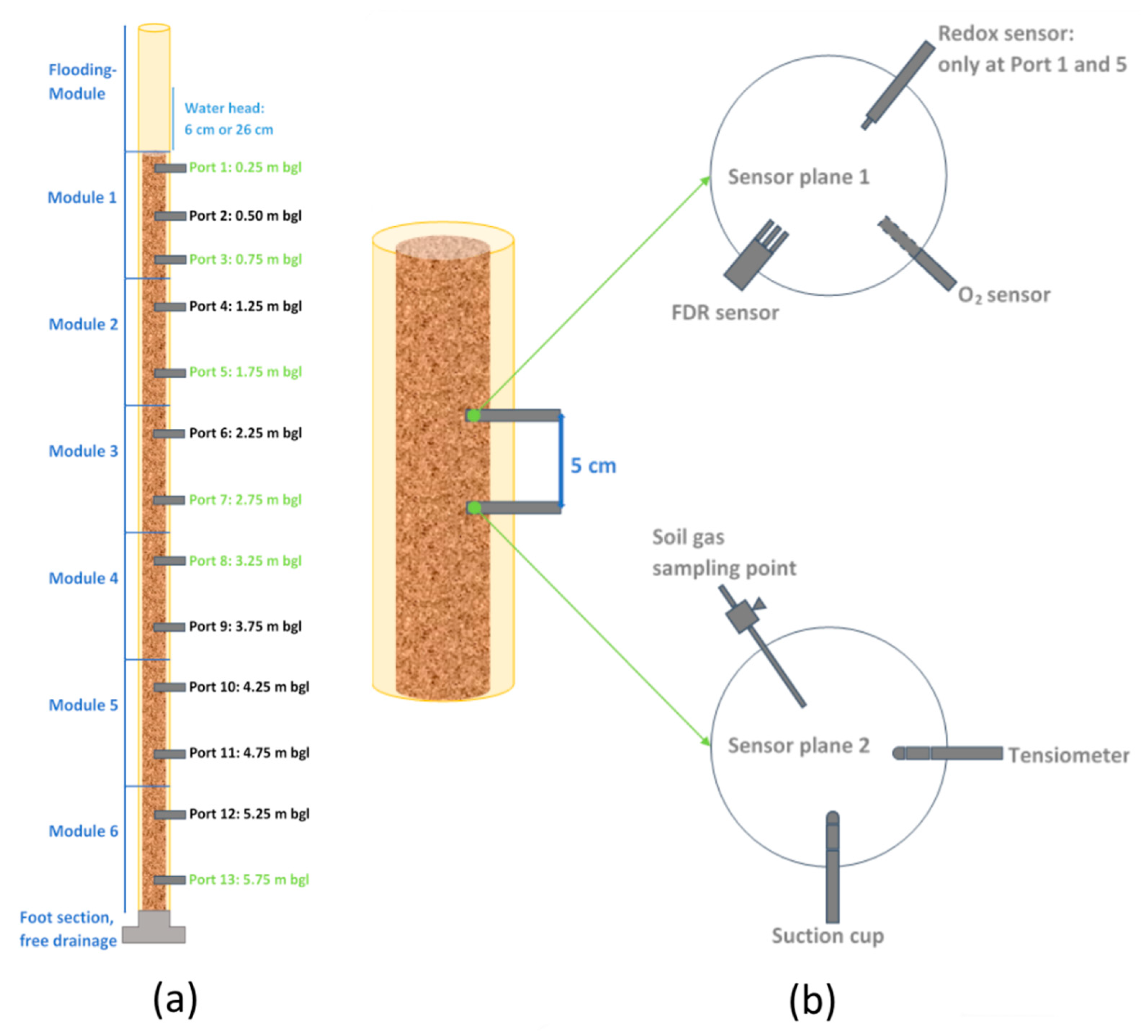
Water, Free Full-Text
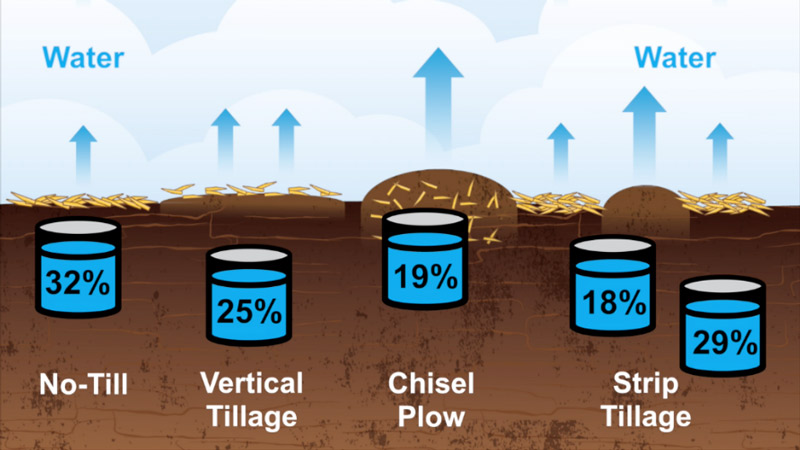
Reducing tillage intensity
NAWM Hydric Soils Online Training Series (NonMembers)
3 STATE OF THE PRACTICE OF GROUND WATER AND SOIL REMEDIATION, Innovations in Ground Water and Soil Cleanup: From Concept to Commercialization

ISO 18325:2015 - Geosynthetics — Test method for the determination of water discharge capacity for

Full article: Experimental study on the effect of soil saturation on the electric permeability coefficient during electroosmosis process

PPT - Evaluating Wick Drain Performance in Virginia Soils PowerPoint Presentation - ID:5480752

Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text

Soil - Wikipedia
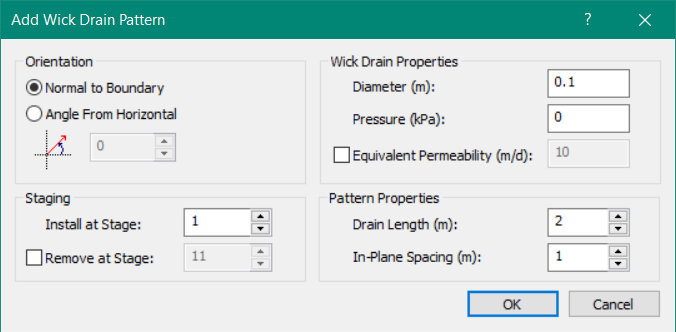
RS2 Documentation Wick Drain Pattern

Hydrophobic Water Repellent Soils are a Problem in Agriculture