
A COMPREHENSIVE QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE EVALUATION OF EXTRAPOLATION OF INTRAVENOUS PHARMACOKINETIC PARAMETERS FROM RAT, DOG, AND MONKEY TO HUMANS. I. CLEARANCE
4.8 (535) In stock

4.8 (535) In stock
This study was conducted to comprehensively survey the available literature on intravenous pharmacokinetic parameters in the rat, dog, monkey, and human, and to compare common methods for extrapolation of clearance, to identify the most appropriate species to use in pharmacokinetic lead optimization, and to ascertain whether adequate prospective measures of predictive success are currently available. One hundred three nonpeptide xenobiotics were identified with intravenous pharmacokinetic data in rat, dog, monkey, and human; both body weight- and hepatic blood flow-based methods were used for scaling of clearance. Allometric scaling approaches, particularly those using data from only two of the preclinical species, were less successful at predicting human clearance than methods based on clearance as a set fraction of liver blood flow from an individual species. Furthermore, commonly used prospective measures of allometric scaling success, including correlation coefficient and allometric exponent, failed to discriminate between successful and failed allometric predictions. In all instances, the monkey tended to provide the most qualitatively and quantitatively accurate predictions of human clearance and also afforded the least biased predictions compared with other species. Additionally, the availability of data from both common nonrodent species (dog and monkey) did not ensure enhanced predictive quality compared with having only monkey data. The observations in this investigation have major implications for pharmacokinetic lead optimization and for prediction of human clearance from in vivo preclinical data and support the continued use of nonhuman primates in preclinical pharmacokinetics.
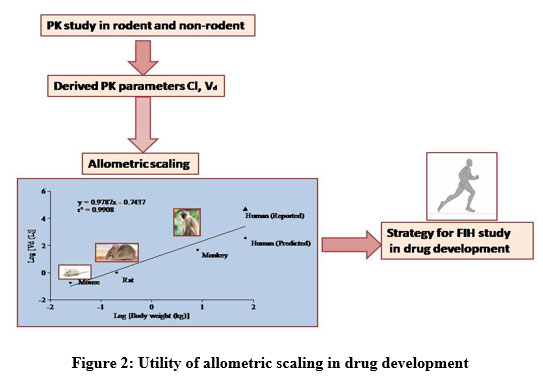
Advantages of Allometric Scaling Methods for Predicting Human Pharmacokinetics of Novel JAK Inhibitor -Baricitinib and Dose Extrapolation – Biomedical and Pharmacology Journal

Predicting the Human Hepatic Clearance of Acidic and Zwitterionic Drugs
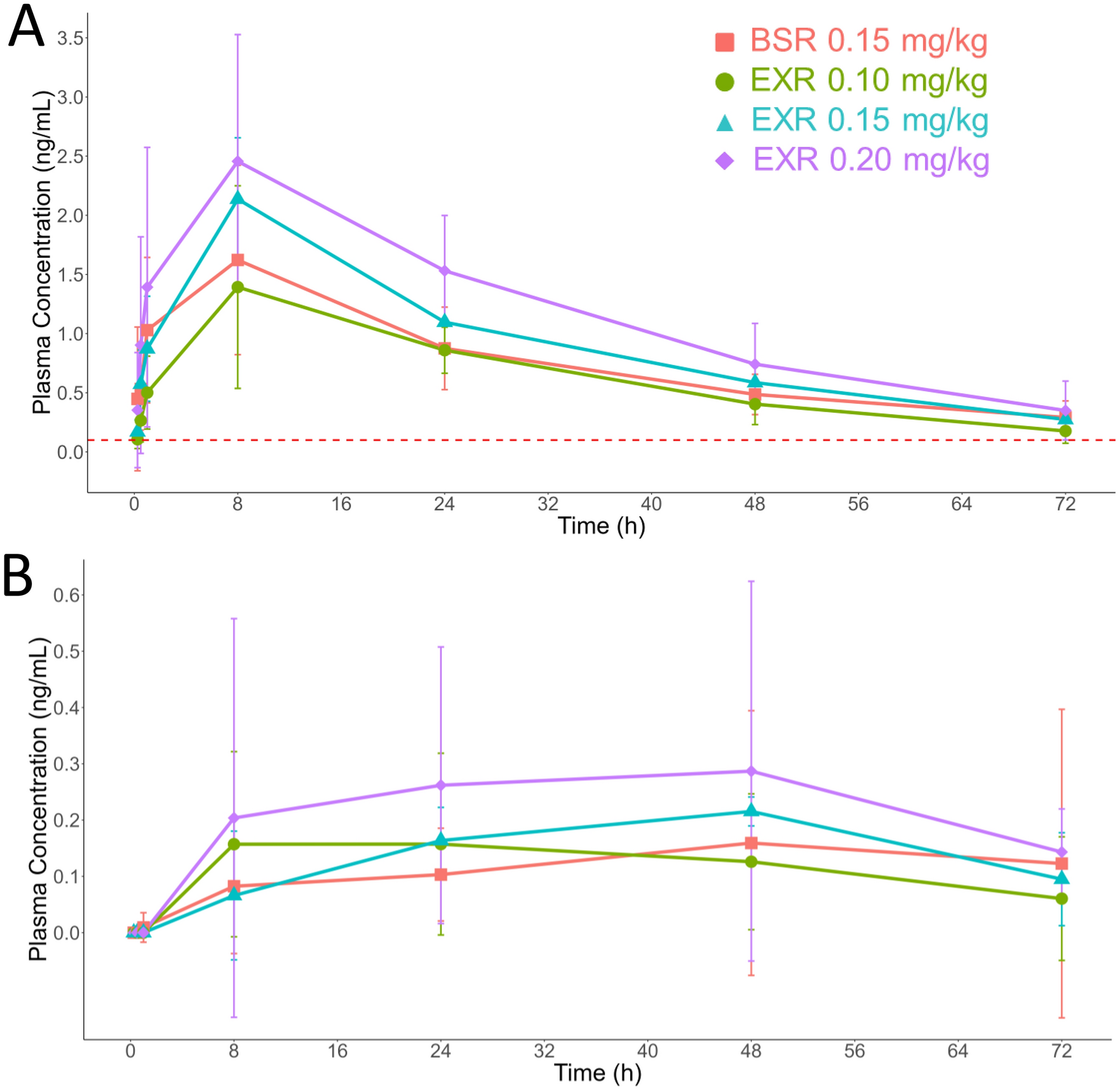
Evaluation and comparison of pharmacokinetic profiles and safety of two extended-release buprenorphine formulations in common marmosets (Callithrix jacchus)
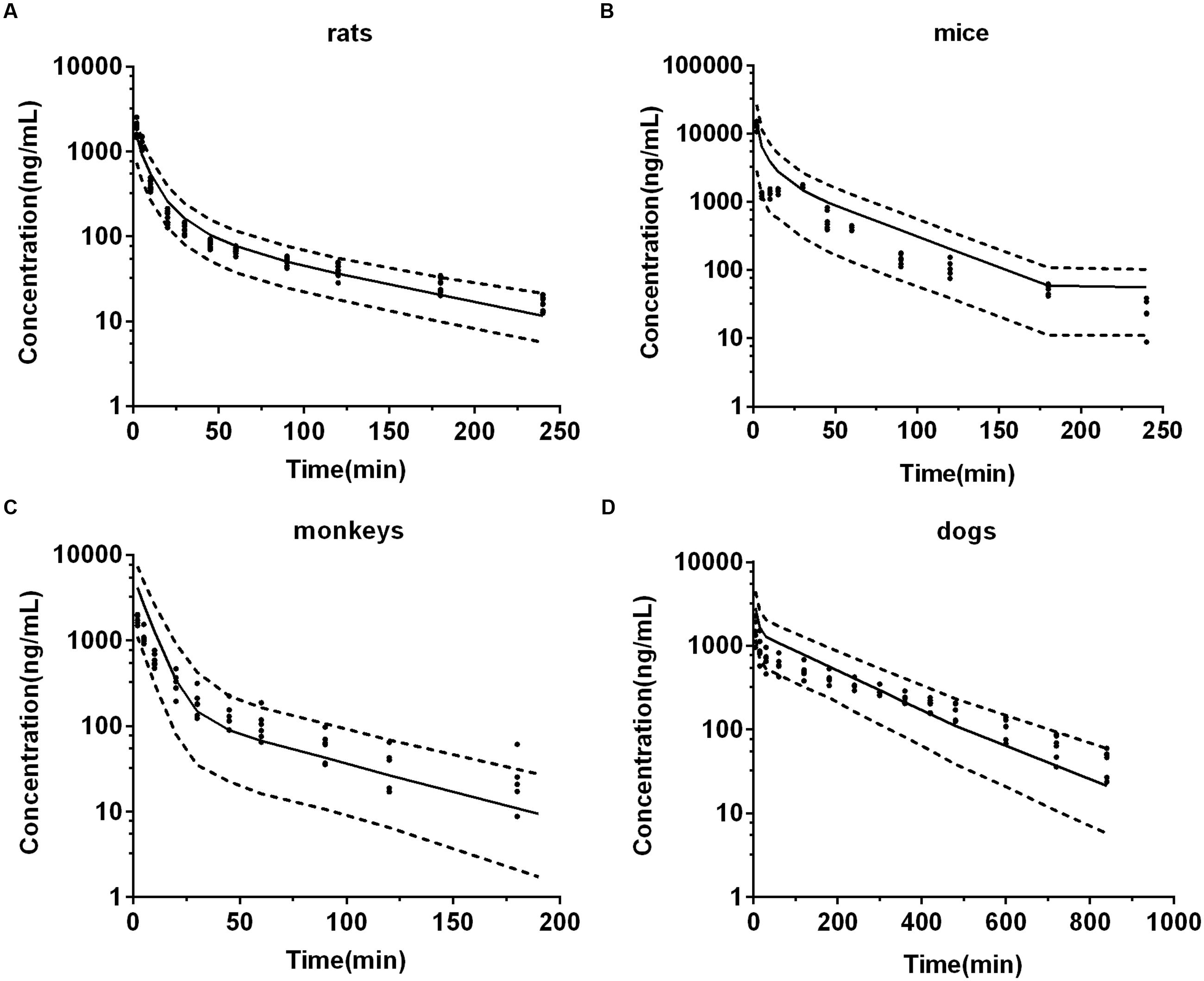
Frontiers Prediction of Deoxypodophyllotoxin Disposition in Mouse, Rat, Monkey, and Dog by Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model and the Extrapolation to Human
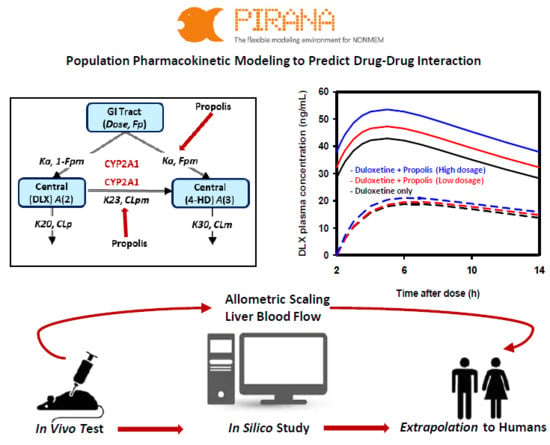
IJMS, Free Full-Text

High Expression of UGT1A1/1A6 in Monkey Small Intestine: Comparison of Protein Expression Levels of Cytochromes P450, UDP-Glucuronosyltransferases, and Transporters in Small Intestine of Cynomolgus Monkey and Human
A novel strategy for physiologically based predictions of human pharmacokinetics - Document - Gale Academic OneFile

Animal to human translation: a systematic scoping review of reported concordance rates, Journal of Translational Medicine

Animal to human translation: a systematic scoping review of reported concordance rates, Journal of Translational Medicine

PDF] Interspecies Prediction of Human Drug Clearance Based on Scaling Data from One or Two Animal Species
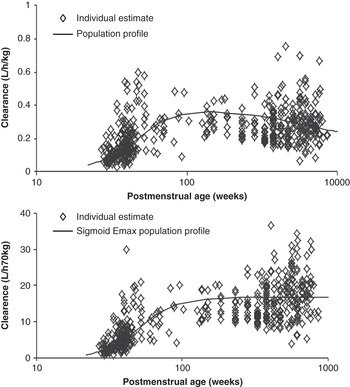
Basic Principles (Section 1) - Personalized Anaesthesia
Interspecies evaluation of a physiologically based pharmacokinetic model to predict the biodistribution dynamics of dendritic nanoparticles
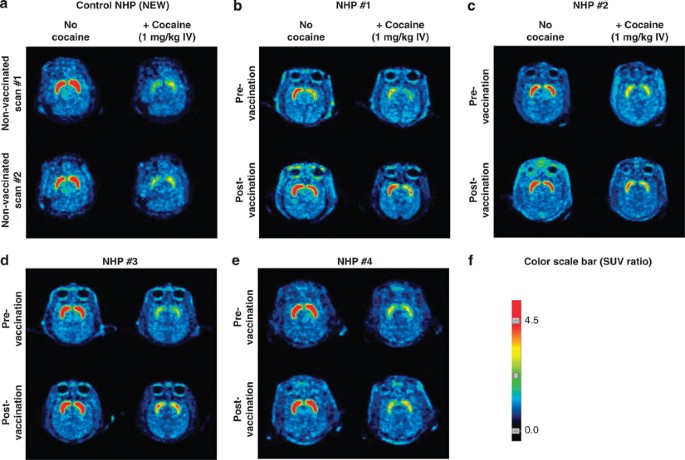
Adenovirus Capsid-Based Anti-Cocaine Vaccine Prevents Cocaine from Binding to the Nonhuman Primate CNS Dopamine Transporter
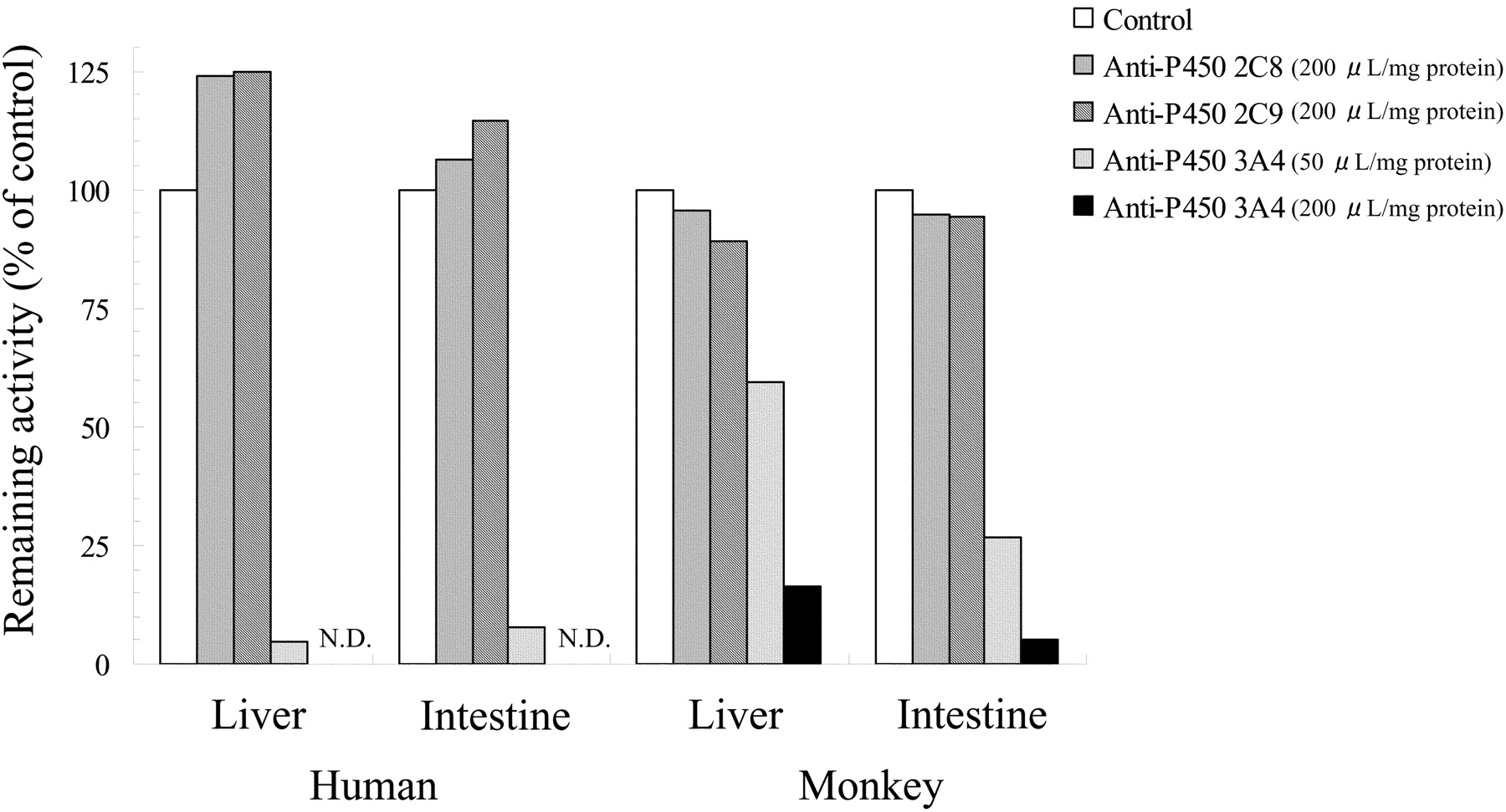
Effect of Oral Ketoconazole on Oral and Intravenous Pharmacokinetics of Simvastatin and Its Acid in Cynomolgus Monkeys

Keith W Ward's research works Reata Pharmaceuticals, Irving and other places